.jpg)
Data Processing Agreement | What is it?
The GDPR requires establishing a Data Processing Agreement (DPA) between the data controller and data processor.
This means that if your organisation uses a product or service provider that requires processing personal data on your behalf, a contract must be established.
-
Data Processing Agreement Template
-
Checklist for Data Processing Agreements
Data Processing Agreements are Required
Organisations interact constantly, buying each other's services and products. These transactions often require a transfer of personal data between the parties to fulfil the service; for example, an external bookkeeper processes the clients' invoices, receipts, etc., which hold the personal data of the buyers and sellers.
When you hire a third party to provide a service involving handling personal data, they must process that data to the same standards you are obligated to meet. This makes sense, as outsourcing the processing of personal data shouldn’t exempt you from your GDPR responsibilities.
That's why the GDPR requires a data processing agreement to govern such outsourcing activities.
In terms of the GDPR, a data processing agreement is made between two parties, which are called data 'controllers' and 'processors'.
Data Controller
A data controller is an organisation responsible for determining the purpose and means of processing personal data.
In practice, all organisations act as data controllers since they manage data related to customers or employees as part of their operations. Personal data must be securely processed within your organisation and when outsourced to a vendor (data processor).
As a data controller, your organisation must ensure that a data processing agreement is in place for outsourcing personal data processing to a data processor.
Data Processor
On the other hand, a data processor is an organisation that processes personal data on behalf of a data controller. Essentially, the data processor manages the personal data that has been outsourced to them by the controller's choice.
Since the data processor handles personal data on behalf of the data controller, it must strictly follow the guidelines set by the data controller.
The data processing agreement should clearly outline these guidelines, which the data processor agrees to when taking on the outsourced work on behalf of the controller.
Examples of Data Processors
Consultancy Firm Using a Bookkeeping Service
Consider a consultancy firm that hires an external bookkeeping service to manage its day-to-day financial records.
In this scenario, the consultancy firm acts as the data controller, while the bookkeeping service functions as the data processor, handling invoices, receipts, and other financial data on behalf of the firm. The bookkeeping service must process this data strictly according to the terms agreed upon with the consultancy firm, as the data belongs to the firm.
Webshop Using a Hosting Provider
A webshop selling shoes to customers would also be a data controller, as it processes personal data to manage purchase orders and ship products.
When this webshop uses a cloud service to host its online platform, the hosting provider becomes the data processor. The hosting provider must process the webshop's customer data according to its instructions, as outlined in their data processing agreement since the data remains the property of the webshop.
What is a Data Processing Agreement (DPA)?
A Data Processing Agreement (DPA) is the term used for a legally binding contract that must be established whenever a data controller outsources personal data to a data processor for processing.
Under Article 28 of the GDPR, a DPA sets out the terms and conditions under which the data processor may handle personal data on behalf of the data controller. It specifies the responsibilities, obligations, and rights of both parties and covers aspects such as security measures, procedures for reporting data breaches, and compliance with GDPR requirements.
In essence, the DPA defines the relationship between the data controller and the data processor, ensuring that the processing of personal data aligns with GDPR standards and that the rights of data subjects are protected.
What is the purpose of having a DPA?
Its primary purpose is to ensure that personal data is processed safely, safeguarding data subjects' rights while promoting trust and transparency when outsourcing the processing of personal data.
The DPA clarifies the roles, responsibilities, and obligations of each party involved in data processing.
This is important to avoid ambiguity over who is accountable for fulfilling various obligations. Without a clear delineation, there’s a risk that no party assumes responsibility or that one party might take on responsibilities they aren’t meant to handle.
Checklist: Data Processing Agreement
There are several requirements for a data processing agreement, but the first requirement is that it must be documented in writing and maintained electronically. This ensures that the agreed terms are properly documented for inspection, audit purposes, and other compliance needs.
As a minimum, the agreement should include the following aspects:
Technical and Organisational Security Measures: Ensure appropriate technical and organisational security measures are in place and according to Article 32 of the GDPR.
Details of Processing: The processing of personal data must be described fully.
- Subject Matter of Processing: A clear explanation of the instructions provided by the data controller to the data processor regarding data processing activities.
- Nature of the Processing: A description of how the data will be processed, covering aspects such as collection, storage, processing, disclosure, or deletion.
- Purpose of the Processing: A statement outlining the specific purposes for processing the data.
- Duration of Processing: A specification of how long the processing will take place.
- Type of Personal Data: A detailed description of the processed data, including the type, source, and category.
Obligations: The two parties' obligations must be described.
- The Parties: A specification of the legal obligations and rights of the data controller and processor.
- Processing Instructions: The processor must process personal data only according to the controller's instructions, including any restrictions on data transfer outside the EU/EEA.
- Confidentiality: Anyone handling personal data must be bound by confidentiality agreements or legal obligations.
Engagement of Sub-processors: The processor's use of sub-processors must be described.
- Approval: Written approval must be obtained from the data controller before engaging a sub-processor.
- Liability for Sub-processors: Sub-processors must be subject to the same data protection obligations through a contract or legal act under EU or Member State law. The initial processor remains fully liable to the controller for the sub-processors performance of these obligations.
Support for Data Subject Rights: The data processor must give assistance to the data controller in meeting obligations to respond to individuals’ requests regarding their data rights.
Compliance with Articles 32 to 36: The data processor must give assistance to the data controller in ensuring data security, managing personal data breaches, conducting impact assessments, and communicating with authorities.
Deletion or Return of Data: At the controller’s request, all personal data must be deleted or returned after processing is complete, unless retention is legally required.
Audit and Compliance: The data processor must provide the data controller with the necessary information to demonstrate compliance with data protection obligations and to support audits. It must also inform the controller if any instructions given to them violate GDPR or other applicable laws.
These requirements are outlined in Article 28 of the GDPR.
Data Processing Agreement Template
The EU has made available ‘Standard Contractual Clauses’, which you can use as a template for creating Data Processing Agreements. If you use these clauses as your Data Processing Agreement, you will have a legal foundation to ensure compliance with the GDPR.
If you go to the European Commission's website using the following link, you will find these templates in the EU languages.
Begin by selecting your preferred language for the template and open the page or pdf, and then scroll down to the section titled “ANNEX.”
This section contains the pre-approved text from the EU, which will ensure that your agreement meets the necessary legal standards. The ANNEX covers several important aspects needed for the DPA, so including all sections, from ANNEX through ANNEX IV, in your agreement is essential.
These sections should be adapted to the specific circumstances of your data processing activities. You must fill in all relevant details and modify any sections to represent the relationship between the controller and processor.
Data Processing Agreement (Word Document)
If you prefer, you can use an alternative data processing agreement template provided by the Danish Data Protection Agency. This template is available in English and comes pre-formatted as a Word document, which may be more convenient for some users.
You can download the Data Processing Agreement template in English by following this link.
Software-as-a-Service and Data Processing Agreements
Many service providers, such as Microsoft Azure and Amazon Web Services, operate as data processors and offer a one-size-fits-all standard data processing agreement for clients. However, it is the responsibility of the data controller to ensure that a suitable data processing agreement is in place.
Changing the Terms of a Data Processing Agreement
In practice, your ability to negotiate these terms with such service providers can be significantly limited. Large providers offer standard agreements that are largely non-negotiable, meaning that if you require their services, you're typically left with no option but to accept their pre-set terms and conditions.
This situation puts you in a challenging position: while you're legally responsible for the data being processed, your control over the terms is often minimal. Although the DPA will outline the processor's obligations and your rights, the extent to which you can influence these terms is usually minimal.
Despite this, it remains essential to carefully review these agreements to understand their impact on your data processing activities.
Choose Your Data Processors Carefully
You must ensure that the terms of these larger providers comply with the GDPR and that the provider’s security measures meet your requirements. If the terms are unsatisfactory, your only viable option might be to look for alternative providers. However, this isn’t always feasible, especially if the services are critical to your operations.
While you are responsible for compliance with data protection regulations, the realities of dealing with large service providers often mean you must accept their terms to continue using their services.
This makes it tricky to source software-as-a-service solutions, which you can read more about in our guide to buying GDPR compliance software.
Smaller Vendors and Data Processing Agreements
When dealing with smaller vendors such as your bookkeeper, marketing agency, or other service providers, you often have more flexibility in negotiating data processing agreements. Unlike large SaaS providers, these vendors are often more willing to customise agreements to address your concerns.
As the data controller, you must assess these vendors and ensure their risk profile aligns with the level of personal data they’ll be processing.
If you collaborate with multiple vendors, it might be worthwhile to develop a standard DPA template that you can use across all agreements. This approach helps maintain consistency in data protection practices and simplifies managing agreements across vendors.
Develop a Standard DPA Template
Having a company-specific template ensures that all DPAs are consistent with your internal policies and compliance requirements. Larger organisations often adopt this approach to manage risks effectively and to maintain control over how data is handled across various vendors. This way, you save time and reduce the chances of overlooking important clauses or requirements in individual agreements.
For smaller organisations without the resources to create a custom template, using a pre-existing one can be a practical solution. However, when using a template, be sure to adapt it to your specific needs, and consider seeking legal advice if you don’t have the necessary in-house expertise.
Although you may have more control over DPAs with smaller vendors, you must ensure these agreements and your processors' conduct comply with the GDPR.
Audit of Data Processors

A sometimes forgotten requirement of the GDPR is to ensure that your data processors comply with the agreement. Remember that these agreements aim to ensure that the processing of personal data outsourced to a supplier cannot lower the standards and protection of personal data.
Therefore, you must audit their compliance with your agreement. You can read more about how to conduct ongoing audits of your Data Processing Agreements here.
Auditing can be a massive undertaking for your company, so how it should be handled deserves your attention.
Penalties for Non-compliance
Failing to follow GDPR rules regarding data processors can lead to significant fines of up to €10 million or 2% of your annual global revenue, whichever is higher.
Non-compliance can manifest in various ways, such as having incorrect agreements with data processors, inadequate oversight of their activities, or failing to thoroughly vet them. Any of these issues could expose your organisation to significant risk.
If a data processor starts making decisions about how data is processed, it essentially takes on the responsibilities of a data controller. In that case, the processor could face the same penalties as a data controller for GDPR breaches.
Additionally, individuals whose data has been mishandled may take legal action, including seeking compensation for any harm they experience, adding further costs and complications for your organisation.
Conclusion
Your organisation should have DPAs for its vendors to process personal data.
If your organisation doesn’t have these agreements, it will not comply with the GDPR.
The checklists and templates referred to in this article can be used to draft thorough DPAs for your organisation or as a starting point in your discussions with legal experts.
Next, after you have established these DPAs, you must conduct regular audits to ensure that they are compliant with your agreement.
FAQs
-
What is a DPA?
A DPA, or Data Processing Agreement, is a contract between a data controller and a data processor.
-
Is a Data Processing Agreement Mandatory?
Yes, under GDPR, a Data Processing Agreement (DPA) is mandatory whenever a data controller engages a data processor to handle tasks that involve processing personal data on their behalf.
A DPA outlines the terms, conditions, and obligations concerning data processing activities between the data controller and the data processor.
Its primary purpose is to ensure compliance with data protection laws and protect data subjects' interests. Failure to establish a DPA when GDPR requires it can lead to sanctions, injunctions, or public exposure for non-compliance.
-
How Often Should DPAs Be Reviewed or Updated?
The frequency of reviewing or updating a DPA depends on several factors, such as changes in processing activities, legal requirements, or the business relationship between the parties involved.
Generally, DPAs should be reviewed regularly to ensure they comply with relevant regulations and reflect the company's current practices and situation.
-
How to Handle Sub-Processors?
According to GDPR, a data controller must have a DPA with every data processor that handles personal data on their behalf.
Suppose one of these data processors engages additional companies, known as sub-processors, to manage the same data. In that case, this must be approved by the data controller and in line with the original agreement.
These sub-processors must comply with the same obligations as the primary data processor to ensure a consistent standard of data protection throughout the entire supply chain.
Outsourcing personal data should not increase the risks of the data subjects at any given time.
-
When is a Data Processing Agreement (DPA) not required?
A data processing agreement (DPA) is not required when the third party determines the means and purposes of processing personal data. In such cases, they act as data controllers rather than data processors.
For example, it’s important to distinguish between scenarios where a consultant is an independent data controller and those where they act as a data processor. If a lawyer receives personal data for a legal proceeding from the client, they are not processing this data on behalf of a data controller. They act as a lawyer, deciding on the information and actions necessary to resolve the legal proceedings.
In this instance, a DPA is not required because the lawyer decides the purposes of processing personal data and is bound by specific rules applicable to their profession. They process the client's data to fulfil their legal obligations, not on behalf of another data controller.
Therefore, a DPA is only necessary when the external party is processing personal data exclusively on behalf of the data controller - which was not the case in this example of the lawyer.
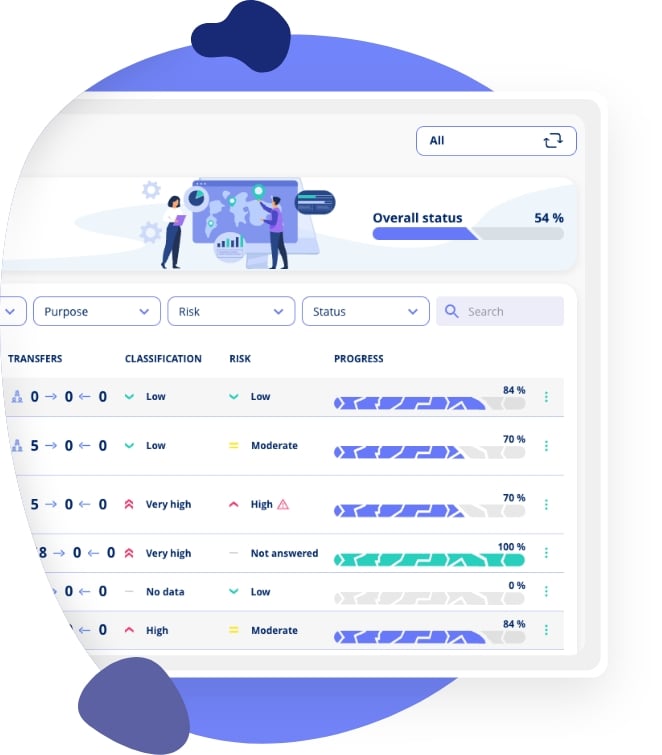
GDPR Compliance Software




.jpeg)
.jpg)
.jpg)



.jpg)

-1.png)



.jpeg)






.jpg)





Info
.legal A/S
hello@dotlegal.com
+45 7027 0127
VAT-no: DK40888888
Support
support@dotlegal.com
+45 7027 0127
Need help?
Let me help you get started

+45 7027 0127 and I'll get you started
.legal is not a law firm and is therefore not under the supervision of the Bar Council.