AI system
The EU’s AI Act sets new rules for how AI (artificial intelligence) can be used by organisations. But before you can follow the rules, you need to know what actually counts as an AI system.

Table of Contents
Definition of an AI system
In simple terms, an AI system is a type of computer programme or machine that can analyse information and make decisions based on what it learns. Unlike traditional software, which simply follows fixed instructions, AI can adapt, improve and make choices depending on the situation.
The AI Act defines an AI system as:
“…a machine-based system that is designed to operate with varying levels of autonomy and that may exhibit adaptiveness after deployment, and that, for explicit or implicit objectives, infers, from the input it receives, how to generate outputs such as predictions, content, recommendations, or decisions that can influence physical or virtual environments.”
How does AI work?
AI systems process data like text, numbers, images or voice commands. For example, a chatbot reads customer messages, a self-driving car detects objects on the road and a weather app predicts tomorrow’s forecast.
As AI processes data, it looks for patterns and learns from experience. The more data it handles, the better it gets at spotting useful patterns, like your film preferences or signs of fraud in financial transactions.
Once the AI has learned from the data, it can:
- Make predictions: "This customer might cancel their subscription soon."
- Give recommendations: "Here’s a song you might like."
- Make decisions: "Approve this loan application."
- Generate content: "Write an email to the customer."
Some AI systems require human oversight, for example when assisting doctors with diagnoses, while others operate autonomously, such as self-driving cars.
AI technologies
Now that we have a general understanding of what an AI system is, it’s useful to look at the AI technologies powering these systems. Several of these technologies often work together in an AI system. For example, a generative AI system combines deep learning and natural language processing.
We will have a look at some of these technologies below.
Machine learning is when AI system learns from data. It finds patterns in the data and uses this knowledge to make predictions or decisions without being explicitly programmed for specific outcomes.
Example: A spam filter that improves by analysing previous emails.
Neural networks are a method that is used in machine learning and that are inspired by how the human brain works. They find patterns and connections in large amounts of data.
Example: Speech recognition software such as Siri or Alexa.
Deep learning uses very large and layered neural networks to recognise images, understand speech or generate content.
Example: Recognising faces in photographs on social media.
Generative AI is capable of creating original content, such as text, images, video or audio. It generates new outputs by learning from vast amounts of existing examples. Generative AI systems mostly use deep learning, which builds on neural networks, so it is a method within machine learning.
Example: ChatGPT or Google Gemini generating text and images from descriptions.
Natural language processing is a technology that understands, interprets and generates human language. It allows humans to interact with computers using everyday language.
Example: Chatbots or virtual assistants that respond naturally to customer questions.
Computer vision is an AI technology that interprets visual information (like images or videos). It thereby enables systems to ‘see’, identify objects and understand visual contexts.
Example: Self-driving cars recognising pedestrians or traffic signs.
Robotics refers to machines powered by AI. It enables the robot to perform physical tasks either autonomously or semi-autonomously. AI helps robots sense their surroundings, make decisions and carry out actions in the real world.
Example: Robotic vacuums or industrial robots in factories.
Examples of AI systems
When systems use these AI technologies to perform tasks like learning, deciding or generating content, they are considered AI systems. Let’s take a closer look at some common examples of AI systems.
Chatbots
AI-powered chatbots can handle customer enquiries without human involvement. These chatbots analyse user data and messages to generate responses based on pre-learned patterns or real-time AI processing.
Technologies used: natural language processing, machine learning
Robot vacuums
Robot vacuums use AI for autonomous navigation, obstacle detection and personalised cleaning routines based on room layouts and past cleaning data.
Technologies used: robotics, computer vision, machine learning
Dynamic pricing
Businesses like airlines and ride-sharing services use AI to adjust prices automatically based on factors such as demand, competitor pricing or user behaviour. These models analyse data such as peak hours, booking trends and historical patterns to set optimal pricing in real time. This then influences consumer decisions and revenue.
Technologies used: machine learning
Content moderation
Social media platforms rely on AI to detect and filter harmful content, including hate speech, misinformation or inappropriate images. AI analyses text, images and videos to determine whether they violate policies and whether they should be flagged, removed or allowed. It can therefore shape what users see online and how users interact online.
Technologies used: natural language processing, computer vision, deep learning
Financial trading
AI is used in finance for algorithmic trading, where it processes market data, identifies trends and executes buy or sell orders automatically. These systems operate at varying levels of autonomy and can make decisions that impact stock markets and investment strategies.
Technologies used: machine learning, deep learning
Cybersecurity
AI helps protect networks by identifying suspicious patterns that may signal cyber threats, such as a hacking attempt or a malware infection. These systems predict risks and recommend or take protective actions by analysing network data.
Technologies used: machine learning
Medical diagnosis
AI is used in healthcare to support healthcare professionals by analysing medical data from X-rays, MRIs and lab reports. It is also used to suggest possible diagnoses, which can impact patient health.
Technologies used: computer vision, deep learning
Predictive maintenance in manufacturing
Manufacturers use AI to anticipate equipment failures, which facilitates proactive maintenance. This is done by analysing sensor data and identifying patterns of wear and tear. AI therefore helps schedule maintenance work, which helps reduce downtime and prevent costly breakdowns.
Technologies used: machine learning, neural networks
HR recruitment
AI can analyse job applications and identify suitable candidates based on factors such as experience, qualifications and skills.
Technologies used: natural language processing, machine learning
Asset inventory management
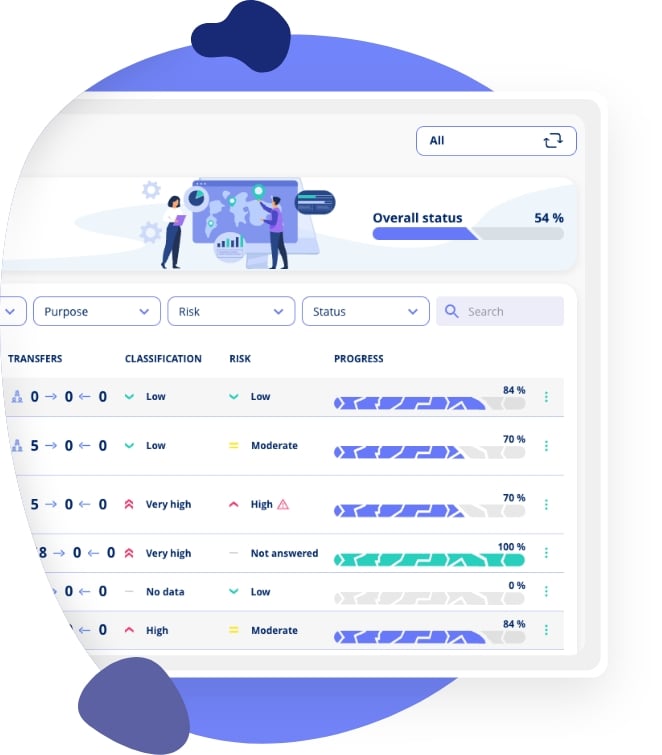
So, what should you do now? You need to find out whether your organisation applies AI systems.
You should start by mapping all assets in your organisation, checking whether they use an AI system and, if they do use AI, how they use it. This gives you the overview you need to understand your responsibilities under the AI Act and find out what actions you need to take to comply.
If you already have an asset inventory from your GDPR compliance, you can reuse it. You simply start adding AI classifications and AI risk assessments to each relevant asset. This then becomes your foundation for compliance with the AI Act.
Once you have mapped your AI systems, you should:
-
Identify if you are acting as a provider or a deployer.
-
Assess the risk level of each AI system.
-
Determine what obligations apply to each system based on its risk level.
Your asset inventory will also help you meet other requirements in the AI Act, such as:
- Identifying which employees work with AI systems so you can provide them with the necessary AI literacy training.
- Documenting and managing high-risk AI systems to fulfil all the specific requirements in the AI Act.
- Ensuring transparency for users where required. For example, if an AI system interacts directly with people or generates content that users could believe comes from a human.
Without this overview, it will be almost impossible to comply properly with the AI Act.
What is an AI system in simple terms?
An AI system is software that can learn from data and make decisions without being explicitly programmed for every scenario. Unlike traditional software that follows fixed rules, AI systems adapt and improve based on the information they process. Examples include chatbots, recommendation engines, and fraud detection tools.
Learn more about AI Act compliance
What are examples of AI systems in everyday business?
Common AI systems include: customer service chatbots, email spam filters, dynamic pricing tools, fraud detection software, personalised marketing recommendations, automated translation services, predictive maintenance systems, and recruitment screening tools. Even basic automation tools might qualify as AI systems if they adapt based on data.
Map your AI systems efficiently
Is ChatGPT considered an AI system?
Yes, ChatGPT and similar tools like Claude, Gemini, and Copilot are AI systems. They're examples of generative AI that create content based on user inputs. If your organisation uses these tools, you need to include them in your AI inventory and assess associated risks, especially regarding data protection and transparency.
Manage AI compliance obligations



.jpeg)
.jpg)
.jpg)



.jpg)

-1.png)



.jpeg)






.jpg)





Info
.legal A/S
hello@dotlegal.com
+45 7027 0127
VAT-no: DK40888888
Support
support@dotlegal.com
+45 7027 0127
Need help?
Let me help you get started

+45 7027 0127 and I'll get you started
.legal is not a law firm and is therefore not under the supervision of the Bar Council.